Low Voltage Switchgear
- Home
- Products
- Low Voltage Switchgear
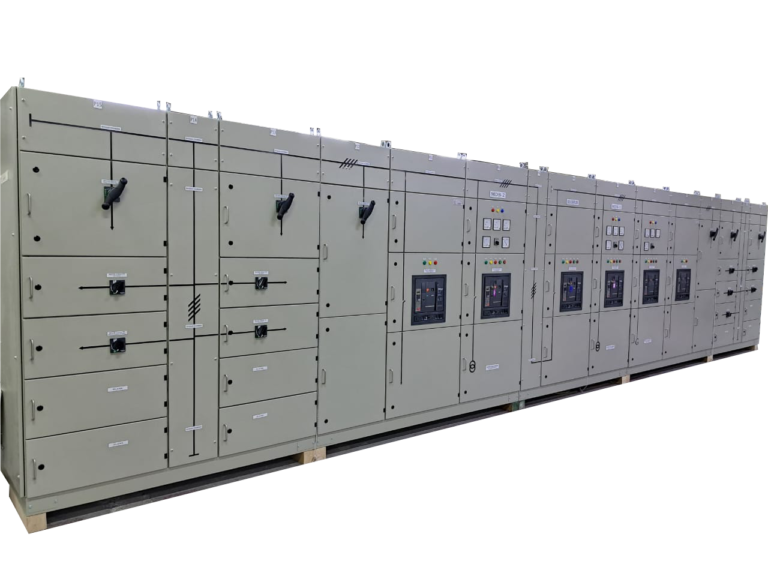
Main Distribution Board (MDB)
A Main Distribution Board (MDB) is an essential component in an electrical distribution system, acting as the central hub for managing and distributing electrical power from a primary source, such as a utility grid or generator, to various circuits within a building or facility. The MDB houses key components like incoming circuit breakers, which control and protect the main power supply, and busbars, which are conductive strips that distribute electricity to multiple outgoing circuits. These outgoing circuits are further protected and controlled by circuit breakers, ensuring safe and reliable power distribution to different parts of the facility. The design and configuration of an MDB are crucial for the efficient and safe operation of the electrical system, making it a vital element in both residential and industrial settings.
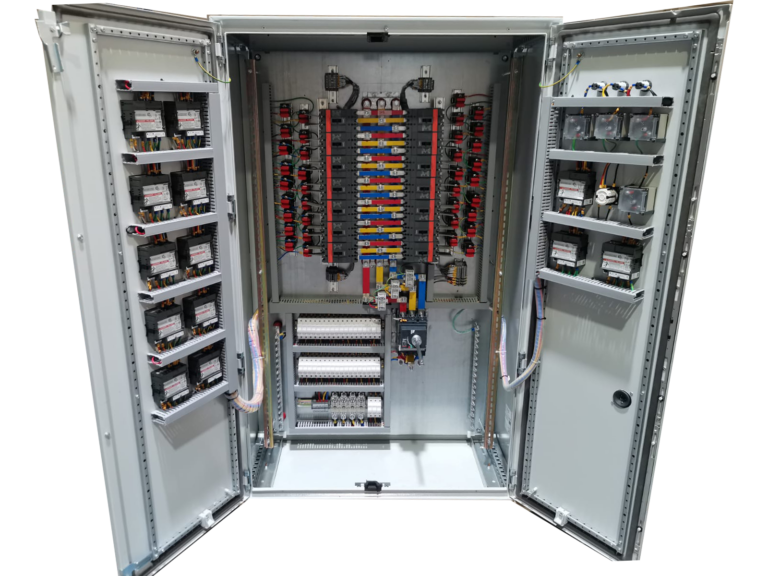


Sub Main Distribution Board (SMDB)
A Sub Main Distribution Board (SMDB) is an integral part of an electrical distribution system, serving as an extension of the Main Distribution Board (MDB). The SMDB takes power from the MDB and distributes it to specific areas or sections of a building, such as different floors or departments. It is equipped with incoming circuit breakers to control the power flow from the MDB, and outgoing circuit breakers to protect and manage the distribution of electricity to sub-circuits or end loads. Busbars within the SMDB facilitate the distribution of power to these circuits. The SMDB is essential for managing electrical loads efficiently, providing localized control, and offering protection against electrical faults like overcurrents and short circuits. This setup allows for greater flexibility in expanding or modifying the electrical system without affecting the entire network, making it especially useful in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and large residential complexes.
Final Distribution Board (FDB)
A Final Distribution Board (FDB) is the point in an electrical system where power is distributed to individual circuits that serve specific areas or devices, such as lighting and outlets. It receives power from an upstream board, like a Main Distribution Board (MDB) or Sub Main Distribution Board (SMDB), and ensures that each circuit is properly protected with circuit breakers or residual current devices (RCDs). These components safeguard the circuits from issues like overcurrents or short circuits, helping to prevent electrical faults from spreading. The FDB is commonly used in homes, offices, and industrial settings to ensure safe and efficient distribution of electricity to end-users.
Motor Control Center (MCC)
A Motor Control Center (MCC) is a centralized system used to manage and control multiple electric motors in industrial settings. It houses several motor control units, each equipped with circuit breakers, motor starters, and protective devices to ensure safe operation. MCCs simplify the wiring and control of motors, improve safety by centralizing control, and facilitate maintenance. They are commonly used in industries like manufacturing and water treatment, where efficient motor management is essential.
Lighting Control Panel (LCP)
A Lighting Control Panel (LCP) is a system used to manage and control lighting circuits within a building or facility. It centralizes the operation of multiple lighting fixtures, allowing for automated or manual control based on specific needs. The LCP typically includes switches, dimmers, timers, and sometimes sensors to optimize energy usage and enhance lighting efficiency. This panel is often used in commercial, industrial, and large residential settings to streamline lighting control, improve energy management, and provide flexibility in adjusting lighting conditions.
Pump Control Panel
A Pump Control Panel is a system designed to manage and control the operation of pumps in various applications, such as water treatment, irrigation, or industrial processes. It centralizes control functions, including starting, stopping, and monitoring pump performance, often using components like motor starters, relays, and overload protection devices. The panel can also include features like automatic level controls, alarms, and variable frequency drives (VFDs) to optimize pump operation and energy efficiency. Pump control panels are essential for ensuring reliable and efficient pump performance, protecting equipment, and simplifying maintenance in various settings.